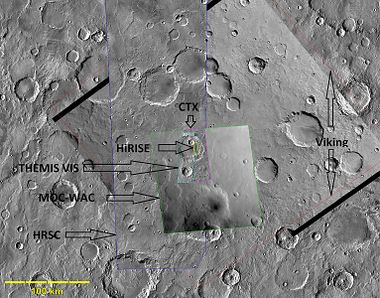
Launched in August of 2005, the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) is flying onboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) mission. By combining very high resolution and signal-to-noise ratio with a large swath width, it is possible to image on a variety of scales down to 1 meter, a scale currently afforded only in glimpses by landers. The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured these sand ripples and the large dune (at center) on Feb. Color has been a.
HiRISE - High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment.The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment Camera is a camera o. The latest tweets from @HiRISE.
February 19, 2021
Figure 1
Mars Hirise Orbiter
The descent stage holding NASA's Perseverance rover can be seen falling through the Martian atmosphere, its parachute trailing behind, in this image taken on Feb. 18, 2021, by the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The ancient river delta, which is the target of the Perseverance mission, can be seen entering Jezero Crater from the left.
HiRISE was approximately 435 miles (700 kilometers) from Perseverance and traveling at about 6750 mile per hour (3 kilometers per second) at the time the image was taken. The extreme distance and high speeds of the two spacecraft were challenging conditions that required precise timing and for Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to both pitch upward and roll hard to the left so that Perseverance was viewable by HiRISE at just the right moment.

The orbiter's mission is led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. JPL, a division of Caltech, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, built the spacecraft. The University of Arizona provided and operates HiRISE.
Embed this resource by pasting the following code into your website:

HiRISE is the most powerful camera ever sent to another planet. From on-board NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) observes the Martian surface at resolutions down to 25 cm/pixel, in three wavelengths and in stereo. The USGS Astrogeology Science Center in Flagstaff, AZ participates in the daily operations of HiRISE and with the processing, distrubution and archiving of this data. View thousands of images and suggest your own at UAHiRISE.org.

Hirise Camera Mars
These images are enhanced color views. The HiRISE camera samples and wavelengths of light that are different than human eyes would see, and the images are stretched to optimize color contrast. The HiRISE bandpasses are 400 - 600 nm (blue - green), 550 - 850 nm (red), 800 - 1000 nm (infrared). The 'RGB' images display the red data as red, the blue - green data as green, and a ratio of the red to blue - green data as blue. In the 'IRB' images, the infrared, red, and blue - green data are displayed in color as red, green and blue respectively.
Hirise Mars Resolution
Image: Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity (arrow) at the southeast rim of Santa Maria crater.
